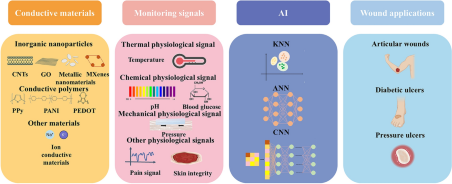
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Conductive Hydrogel Dressings for Refractory Wounds Monitoring
Corresponding Author: Kai Zhang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 17 (2025), Article Number: 319
Abstract
Refractory wounds cause significant harm to the health of patients and the most common treatments in clinical practice are surgical debridement and wound dressings. However, certain challenges, including surgical difficulty, lengthy recovery times, and a high recurrence rate persist. Conductive hydrogel dressings with combined monitoring and therapeutic properties have strong advantages in promoting wound healing due to the stimulation of endogenous current on wounds and are the focus of recent advancements. Therefore, this review introduces the mechanism of conductive hydrogel used for wound monitoring and healing, the materials selection of conductive hydrogel dressings used for wound monitoring, focuses on the conductive hydrogel sensor to monitor the output categories of wound status signals, proving invaluable for non-invasive, real-time evaluation of wound condition to encourage wound healing. Notably, the research of artificial intelligence (AI) model based on sensor derived data to predict the wound healing state, AI makes use of this abundant data set to forecast and optimize the trajectory of tissue regeneration and assess the stage of wound healing. Finally, refractory wounds including pressure ulcers, diabetes ulcers and articular wounds, and the corresponding wound monitoring and healing process are discussed in detail. This manuscript supports the growth of clinically linked disciplines and offers motivation to researchers working in the multidisciplinary field of conductive hydrogel dressings.
Highlights:
1 The advantages and selection of conductive materials, including conductive polymers and inorganic nanoparticles are discussed in detail.
2 Signal output categories of the conductive hydrogel dressing to monitor wound conditions, notably, AI-based wound monitoring and prediction is highlighted.
3 The review analyzes the application, current challenges and potential prospects of conductive hydrogel dressings for the different refractory wounds monitoring.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- P. Wang, B. Yin, Y.J. Su, C.Y. Jia, Research advances in healing mechanism of chronic refractory wounds mediated by long non-coding RNA. Chin. J. Burn. 36(8), 758–761 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20190526-00254
- W. Yue, Y. Guo, J.C. Lee, E. Ganbold, J.K. Wu et al., Advancements in passive wireless sensing systems in monitoring harsh environment and healthcare applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 106 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01599-8
- M. Rodrigues, N. Kosaric, C.A. Bonham, G.C. Gurtner, Wound healing: a cellular perspective. Physiol. Rev. 99(1), 665–706 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00067.2017
- S. Guo, L.A. DiPietro, Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 89(3), 219–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509359125
- K. Las Heras, M. Igartua, E. Santos-Vizcaino, R.M. Hernandez, Chronic wounds: current status, available strategies and emerging therapeutic solutions. J. Control. Release 328, 532–550 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.09.039
- E.M. Ahmed, Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J. Adv. Res. 6(2), 105–121 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
- M. Farahani, A. Shafiee, Wound healing: from passive to smart dressings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10(16), 2100477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202100477
- Y. Qiao, J. Luo, T. Cui, H. Liu, H. Tang et al., Soft electronics for health monitoring assisted by machine learning. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01029-1
- Q. Pang, D. Lou, S. Li, G. Wang, B. Qiao et al., Smart flexible electronics-integrated wound dressing for real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment of infected wounds. Adv. Sci. 7(6), 1902673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902673
- D. Chouhan, N. Dey, N. Bhardwaj, B.B. Mandal, Emerging and innovative approaches for wound healing and skin regeneration: current status and advances. Biomaterials 216, 119267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119267
- J. Hu, H. Qian, S. Han, P. Zhang, Y. Lu, Light-activated virtual sensor array with machine learning for non-invasive diagnosis of coronary heart disease. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 274 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01481-7
- J. Zhu, H. Zhou, E.M. Gerhard, S. Zhang, F.I. Parra Rodríguez et al., Smart bioadhesives for wound healing and closure. Bioact. Mater. 19, 360–375 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.04.020
- M. Falcone, B. De Angelis, F. Pea, A. Scalise, S. Stefani et al., Challenges in the management of chronic wound infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 26, 140–147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2021.05.010
- R. Basatneh, B. Najafi, D.G. Armstrong, Health sensors, smart home devices, and the Internet of medical things: an opportunity for dramatic improvement in care for the lower extremity complications of diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 12(3), 577–586 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296818768618
- C. Wang, E.S. Sani, W. Gao, Wearable bioelectronics for chronic wound management. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(17), 2111022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202111022
- W. Qiu, Q. Wang, M. Li, N. Li, X. Wang et al., 3D hybrid scaffold with aligned nanofiber yarns embedded in injectable hydrogels for monitoring and repairing chronic wounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 234, 109688 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109688
- J. Wang, C. Zhao, P. Yang, H. He, Y. Yang et al., A multifunctional electronic dressing with textile-like structure for wound pressure monitoring and treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 679, 737–747 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2024.10.116
- X. Liu, S. Tian, S. Xu, W. Lu, C. Zhong et al., A pressure-resistant zwitterionic skin sensor for domestic real-time monitoring and pro-healing of pressure injury. Biosens. Bioelectron. 214, 114528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114528
- W. Ma, S. Ling, Y. Liu, Z. Chen, J. Xu, Bio-inspired low-cost fabrication of stretchable, adhesive, transparent, and multi-functionalized joint wound dressings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15(19), 22915–22928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c02065
- D. Prakashan, A. Kaushik, S. Gandhi, Smart sensors and wound dressings: artificial intelligence-supported chronic skin monitoring—a review. Chem. Eng. J. 497, 154371 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154371
- O. Eskilson, E. Zattarin, L. Berglund, K. Oksman, K. Hanna et al., Nanocellulose composite wound dressings for real-time pH wound monitoring. Mater. Today Bio 19, 100574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100574
- Z. Bai, X. Wang, M. Huang, Y. Feng, S. Sun et al., Smart battery-free and wireless bioelectronic platform based on a nature-skin-derived organohydrogel for chronic wound diagnosis, assessment, and accelerated healing. Nano Energy 118, 108989 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108989
- P. Mostafalu, A. Tamayol, R. Rahimi, M. Ochoa, A. Khalilpour et al., Smart bandage for monitoring and treatment of chronic wounds. Small 14(33), 1703509 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703509
- Y. Zhu, J. Zhang, J. Song, J. Yang, Z. Du et al., A multifunctional pro-healing zwitterionic hydrogel for simultaneous optical monitoring of pH and glucose in diabetic wound treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(6), 1905493 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201905493
- Y. Gao, D.T. Nguyen, T. Yeo, S.B. Lim, W.X. Tan et al., A flexible multiplexed immunosensor for point-of-care in situ wound monitoring. Sci. Adv. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abg9614
- L. Wang, M. Zhou, T. Xu, X. Zhang, Multifunctional hydrogel as wound dressing for intelligent wound monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134625 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134625
- S. Kalasin, P. Sangnuang, W. Surareungchai, Intelligent wearable sensors interconnected with advanced wound dressing bandages for contactless chronic skin monitoring: artificial intelligence for predicting tissue regeneration. Anal. Chem. 94(18), 6842–6852 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00782
- J. Jiang, J. Ding, X. Wu, M. Zeng, Y. Tian et al., Flexible and temperature-responsive hydrogel dressing for real-time and remote wound healing monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 11(22), 4934–4945 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB00099K
- H. Ma, Z. Liu, X. Lu, S. Zhang, C. Tang et al., 3D printed multi-coupled bioinspired skin-electronic interfaces with enhanced adhesion for monitoring and treatment. Acta Biomater. 187, 183–198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2024.08.048
- D. Deng, L. Liang, K. Su, H. Gu, X. Wang et al., Smart hydrogel dressing for machine learning-enabled visual monitoring and promote diabetic wound healing. Nano Today 60, 102559 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102559
- M. Wei, H. Wang, C. Chen, G. Fei, D. Yang et al., Conductive, adhesive, and biocompatible hydrogel sensor based on zwitterionic for effective wound healing and monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 506, 160235 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.160235
- Z. Li, L.-P. Sun, Y. Tan, Z. Wang, X. Yang et al., Flexible optoelectronic hybrid microfiber long-period grating multimodal sensor. Adv. Sci. 12(17), e2501352 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202501352
- B.K. Sun, Z. Siprashvili, P.A. Khavari, Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science 346(6212), 941–945 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1253836
- R. Nuccitelli, A role for endogenous electric fields in wound healing. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 58, 1–26 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0070-2153(03)58001-2
- C. Korupalli, H. Li, N. Nguyen, F.-L. Mi, Y. Chang et al., Conductive materials for healing wounds: their incorporation in electroactive wound dressings, characterization, and perspectives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10(6), 2001384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202001384
- J. Wang, J. Lin, L. Chen, L. Deng, W. Cui, Endogenous electric-field-coupled electrospun short fiber via collecting wound exudation. Adv. Mater. 34(9), e2108325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202108325
- X. Zhao, H. Wu, B. Guo, R. Dong, Y. Qiu et al., Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 122, 34–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.011
- N.C. Spitzer, Electrical activity in early neuronal development. Nature 444(7120), 707–712 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05300
- I. Jun, S. Jeong, H. Shin, The stimulation of myoblast differentiation by electrically conductive sub-micron fibers. Biomaterials 30(11), 2038–2047 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.063
- Y. Liang, B. Chen, M. Li, J. He, Z. Yin et al., Injectable antimicrobial conductive hydrogels for wound disinfection and infectious wound healing. Biomacromol 21(5), 1841–1852 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01732
- H. Cui, L. Cui, P. Zhang, Y. Huang, Y. Wei et al., In situ electroactive and antioxidant supramolecular hydrogel based on cyclodextrin/copolymer inclusion for tissue engineering repair. Macromol. Biosci. 14(3), 440–450 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201300366
- X. Ren, M. Xiao, Y. Xu, Y. Wu, J. Yang et al., Injectable MXene conductive hydrogel improves myocardial infarction through scavenging ROS and repairing myocardium electrical integrity. Chem. Eng. J. 481, 148791 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.148791
- W. Liu, N. Zhao, Q. Yin, X. Zhao, K. Guo et al., Injectable hydrogels encapsulating dual-functional Au@Pt core-shell nanops regulate infarcted microenvironments and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of stem cells through antioxidant and electrical integration. ACS Nano 17(3), 2053–2066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c07436
- L. Nie, Q. Wei, J. Li, Y. Deng, X. He et al., Fabrication and desired properties of conductive hydrogel dressings for wound healing. RSC Adv. 13(13), 8502–8522 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA07195A
- L. Lipani, B.G.R. Dupont, F. Doungmene, F. Marken, R.M. Tyrrell et al., Non-invasive, transdermal, path-selective and specific glucose monitoring via a graphene-based platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13(6), 504–511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0112-4
- A. McLister, J. McHugh, J. Cundell, J. Davis, New developments in smart bandage technologies for wound diagnostics. Adv. Mater. 28(27), 5732–5737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201504829
- X. Wang, H. Huo, C. Xu, H. Lin, Q. Wang et al., A sensitive non-enzymatic dual-conductive biosensor for continuous glucose monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 1279, 341845 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341845
- K. Shen, Z. Liu, R. Xie, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang et al., Nanocomposite conductive hydrogels with Robust elasticity and multifunctional responsiveness for flexible sensing and wound monitoring. Mater. Horiz. 10(6), 2096–2108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MH00192J
- Z. Qin, X. Sun, Q. Yu, H. Zhang, X. Wu et al., Carbon nanotubes/hydrophobically associated hydrogels as ultrastretchable, highly sensitive, stable strain, and pressure sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(4), 4944–4953 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21659
- M.F.L. De Volder, S.H. Tawfick, R.H. Baughman, A.J. Hart, Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339(6119), 535–539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222453
- H. Cai, D. Zhang, H. Zhang, M. Tang, Z. Xu et al., Trehalose-enhanced ionic conductive hydrogels with extreme stretchability, self-adhesive and anti-freezing abilities for both flexible strain sensor and all-solid-state supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 472, 144849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.144849
- Z. Xu, X. Qiao, R. Tao, Y. Li, S. Zhao et al., A wearable sensor based on multifunctional conductive hydrogel for simultaneous accurate pH and tyrosine monitoring in sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 234, 115360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115360
- X. Fan, L. Zhao, Q. Ling, J. Liu, H. Gu, Mussel-induced nano-silver antibacterial, self-healing, self-adhesive, anti-freezing, and moisturizing dual-network organohydrogel based on SA-PBA/PVA/CNTs as flexible wearable strain sensors. Polymer 256, 125270 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125270
- J. Wang, W. Liu, G. Luo, Z. Li, C. Zhao et al., Synergistic effect of well-defined dual sites boosting the oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 11(12), 3375–3379 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EE02656D
- H. Sun, Y. Zhao, S. Jiao, C. Wang, Y. Jia et al., Environment tolerant conductive nanocomposite organohydrogels as flexible strain sensors and power sources for sustainable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(24), 2101696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202101696
- W.-L. Lei, C.-W. Peng, S.-C. Chiu, H.-E. Lu, C.-W. Wu et al., All biodisintegratable hydrogel biohybrid neural interfaces with synergistic performances of microelectrode array technologies, tissue scaffolding, and cell therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(3), 2307365 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202307365
- F. He, X. You, H. Gong, Y. Yang, T. Bai et al., Stretchable, biocompatible, and multifunctional silk fibroin-based hydrogels toward wearable strain/pressure sensors and triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(5), 6442–6450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b19721
- Z. Tu, M. Chen, M. Wang, Z. Shao, X. Jiang et al., Engineering bioactive M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial scaffolds for rapid angiogenesis and diabetic wound repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(30), 2100924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202100924
- L. Geng, W. Liu, B. Fan, J. Wu, S. Shi et al., Anisotropic double-network hydrogels integrated superior performance of strength, toughness and conductivity for flexible multi-functional sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 462, 142226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142226
- Y. Zhang, J. Zou, S. Wang, X. Hu, Z. Liu et al., Tailoring nanostructured MXene to adjust its dispersibility in conductive hydrogel for self-powered sensors. Compos. Part B Eng. 272, 111191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2024.111191
- Y. Zhang, Z. Xu, Y. Yuan, C. Liu, M. Zhang et al., Flexible antiswelling photothermal-therapy MXene hydrogel-based epidermal sensor for intelligent human–machine interfacing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(21), 2300299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202300299
- J. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Zhou, S. Zhu, C. Gao et al., A multifunctional sensor for real-time monitoring and pro-healing of frostbite wounds. Acta Biomater. 172, 330–342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2023.10.003
- B. Song, X. Fan, J. Shen, H. Gu, Ultra-stable and self-healing coordinated collagen-based multifunctional double-network organohydrogel e-skin for multimodal sensing monitoring of strain-resistance, bioelectrode, and self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator. Chem. Eng. J. 474, 145780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145780
- Y. Zhao, Z. Li, S. Song, K. Yang, H. Liu et al., Skin-inspired antibacterial conductive hydrogels for epidermal sensors and diabetic foot wound dressings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(31), 1901474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901474
- X. Wang, H. Huo, Y. Zhong, Y. Yang, H. Lin et al., Synergistic antimicrobial glycyrrhizic acid-based functional biosensing composite for sensitive glucose monitoring and collaborative wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(20), 2400580 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202400580
- Y. Zhang, S. Li, Z. Gao, D. Bi, N. Qu et al., Highly conductive and tough polyacrylamide/sodium alginate hydrogel with uniformly distributed polypyrrole nanospheres for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 315, 120953 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120953
- J. Xu, H. Zhang, Z. Guo, C. Zhang, H. Tan et al., Fully physical crosslinked BSA-based conductive hydrogels with high strength and fast self-recovery for human motion and wireless electrocardiogram sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 230, 123195 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123195
- H. Zheng, M. Chen, Y. Sun, B. Zuo, Self-Healing, Wet-Adhesion silk fibroin conductive hydrogel as a wearable strain sensor for underwater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136931 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136931
- H. He, H. Li, A. Pu, W. Li, K. Ban et al., Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 14(1), 759 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36438-8
- H. Liu, Z. Li, S. Che, Y. Feng, L. Guan et al., A smart hydrogel patch with high transparency, adhesiveness and hemostasis for all-round treatment and glucose monitoring of diabetic foot ulcers. J. Mater. Chem. B 10(30), 5804–5817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TB01048H
- L.S. Devi, R.P. Palathinkal, A.K. Dasmahapatra, Preparation of cross-linked PANI/PVA conductive hydrogels for electrochemical energy storage and sensing applications. Polymer 293, 126673 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2024.126673
- H. Zhang, H. Shen, J. Lan, H. Wu, L. Wang et al., Dual-network polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan-grafted-polyaniline conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 295, 119848 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119848
- L. Xiao, F. Hui, T. Tian, R. Yan, J. Xin et al., A novel conductive antibacterial nanocomposite hydrogel dressing for healing of severely infected wounds. Front. Chem. 9, 787886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.787886
- X. Peng, W. Wang, W. Yang, J. Chen, Q. Peng et al., Stretchable, compressible, and conductive hydrogel for sensitive wearable soft sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 618, 111–120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.03.037
- G. Li, K. Huang, J. Deng, M. Guo, M. Cai et al., Highly conducting and stretchable double-network hydrogel for soft bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 34(15), 2200261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202200261
- C. Zhang, M. Wang, C. Jiang, P. Zhu, B. Sun et al., Highly adhesive and self-healing γ-PGA/PEDOT: PSS conductive hydrogels enabled by multiple hydrogen bonding for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 95, 106991 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.106991
- Y. Shin, H.S. Lee, J.-U. Kim, Y.-H. An, Y.-S. Kim et al., Functional-hydrogel-based electronic-skin patch for accelerated healing and monitoring of skin wounds. Biomaterials 314, 122802 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122802
- Y. Wang, L. Sun, G. Chen, H. Chen, Y. Zhao, Structural color ionic hydrogel patches for wound management. ACS Nano 17(2), 1437–1447 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c10142
- W. Zou, Y. Zhou, S. Zhong, F. Liao, J. Lu et al., Biomimetic FeNi-MOF assisted intelligent theranostic hydrogels for pH identification and treatment of wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 497, 154945 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154945
- H. Zhang, H. Hu, Y. Dai, L. Xin, Q. Pang et al., A conductive multifunctional hydrogel dressing with the synergistic effect of ROS-scavenging and electroactivity for the treatment and sensing of chronic diabetic wounds. Acta Biomater. 167, 348–360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.045
- H.-M. Zhang, Y.-P. Wang, S.-F. Zhang, W.-B. Niu, Heterogeneous structural color conductive photonic organohydrogel fibers with alternating single and dual networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(49), 54936–54945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c16191
- X. Zhang, H. Geng, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Hao et al., Modulation of double-network hydrogels via seeding calcium carbonate microps for the engineering of ultrasensitive wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 11(6), 2996–3007 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TA07834A
- Y.-H. Lin, Y.-C. Chen, K.-S. Cheng, P.-J. Yu, J.-L. Wang et al., Higher periwound temperature associated with wound healing of pressure ulcers detected by infrared thermography. J. Clin. Med. 10(13), 2883 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132883
- N. Kučišec-Tepeš, Characteristic features of pressure ulcer infection. Acta Med. Croat. 70(Suppl 1), 45–51 (2016). (PMID: 29087671)
- N. Li, Y. Li, Z. Cheng, Y. Liu, Y. Dai et al., Bioadhesive polymer semiconductors and transistors for intimate biointerfaces. Science 381(6658), 686–693 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg8758
- J.L. Ramirez-GarciaLuna, R. Bartlett, J.E. Arriaga-Caballero, R.D.J. Fraser, G. Saiko, Infrared thermography in wound care, surgery, and sports medicine: a review. Front. Physiol. 13, 838528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.838528
- F.R. Ávila, M.T. Huayllani, D. Boczar, P. Ciudad, R. Sarabia-Estrada et al., Materiales sensibles a biomarcadores y apósitos inteligentes: revisión sistemática. J. Wound Care 29(LatAm sup 3), 13–22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2020.29.LatAm_sup_3.13
- T. Kanazawa, A. Kitamura, G. Nakagami, T. Goto, T. Miyagaki et al., Lower temperature at the wound edge detected by thermography predicts undermining development in pressure ulcers: a pilot study. Int. Wound J. 13(4), 454–460 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12454
- F.-Q. Yang, L. Ge, Colorimetric sensors: methods and applications. Sensors 23(24), 9887 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249887
- F. Mo, P. Zhou, S. Lin, J. Zhong, Y. Wang, A review of conductive hydrogel-based wearable temperature sensors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(26), e2401503 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202401503
- H. Chen, J. Huang, J. Liu, J. Gu, J. Zhu et al., High toughness multifunctional organic hydrogels for flexible strain and temperature sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 9(40), 23243–23255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA07127K
- X. Dang, Y. Fu, X. Wang, Versatile biomass-based injectable photothermal hydrogel for integrated regenerative wound healing and skin bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(42), 2405745 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202405745
- M.-H. Schmid-Wendtner, H.C. Korting, The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier function. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 19(6), 296–302 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1159/000094670
- S.L. Percival, S. McCarty, J.A. Hunt, E.J. Woods, The effects of pH on wound healing, biofilms, and antimicrobial efficacy. Wound Repair Regen. 22(2), 174–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.12125
- Q. Dou, Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Wang, D. Hu et al., Ultrasensitive poly(boric acid) hydrogel-coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor by using UV pressing-assisted polymerization for saliva glucose monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(30), 34190–34197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c08229
- H. Guo, M. Bai, C. Wen, M. Liu, S. Tian et al., A Zwitterionic-Aromatic Motif-Based ionic skin for highly biocompatible and Glucose-Responsive sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 561–571 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.012
- P. Martin, Wound healing: aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276(5309), 75–81 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5309.75
- B. Hajhosseini, M.T. Longaker, G.C. Gurtner, Pressure injury. Ann. Surg. 271(4), 671–679 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000003567
- G.S. Schultz, R.G. Sibbald, V. Falanga, E.A. Ayello, C. Dowsett et al., Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair Regen. 11(s1), S1–S28 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-475X.11.s2.1.x
- Q. Zeng, X. Qi, G. Shi, M. Zhang, H. Haick, Wound dressing: from nanomaterials to diagnostic dressings and healing evaluations. ACS Nano 16(2), 1708–1733 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c08411
- Q. Wang, W. Qiu, H. Liu, X. Li, X. Qin et al., Conductive hydrogel dressings based on cascade reactions with photothermal effect for monitoring and treatment of diabetic wounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 242, 110098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110098
- S.-J. Ge, X.-J. Zhou, S.-L. Liu, M. Xu, Y. Shi et al., Multifunctional all hydrogel-based smart dressing system fabricated by a self-healing cross-linking strategy for real-time monitoring of wound temperature, strain and on-demand drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. C 10(45), 17084–17098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TC03887K
- A. Kekonen, M. Bergelin, J.-E. Eriksson, A. Vaalasti, H. Ylänen et al., Bioimpedance method for monitoring venous ulcers: Clinical proof-of-concept study. Biosens. Bioelectron. 178, 112974 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.112974
- S.L. Swisher, M.C. Lin, A. Liao, E.J. Leeflang, Y. Khan et al., Impedance sensing device enables early detection of pressure ulcers in vivo. Nat. Commun. 6, 6575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7575
- J. Cao, P. Wu, Q. Cheng, C. He, Y. Chen et al., Ultrafast fabrication of self-healing and injectable carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel dressing for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(20), 24095–24105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c02089
- L. Zhao, L. Niu, H. Liang, H. Tan, C. Liu et al., pH and glucose dual-responsive injectable hydrogels with insulin and fibroblasts as bioactive dressings for diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(43), 37563–37574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09395
- O. Simoska, J. Duay, K.J. Stevenson, Electrochemical detection of multianalyte biomarkers in wound healing efficacy. ACS Sens. 5(11), 3547–3557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01697
- J. Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. Lee, J. Hua, S. Li et al., A pulsatile release platform based on photo-induced imine-crosslinking hydrogel promotes scarless wound healing. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1670 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21964-0
- S. Du, N. Zhou, Y. Gao, G. Xie, H. Du et al., Bioinspired hybrid patches with self-adhesive hydrogel and piezoelectric nanogenerator for promoting skin wound healing. Nano Res. 13(9), 2525–2533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2891-9
- L. Mao, S. Hu, Y. Gao, L. Wang, W. Zhao et al., Biodegradable and electroactive regenerated bacterial cellulose/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) composite hydrogel as wound dressing for accelerating skin wound healing under electrical stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9(19), 2000872 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000872
- B. Qiao, Q. Pang, P. Yuan, Y. Luo, L. Ma, Smart wound dressing for infection monitoring and NIR-triggered antibacterial treatment. Biomater. Sci. 8(6), 1649–1657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm02060h
- E.S. Sani, C. Wang, W. Gao, A soft bioaffinity sensor array for chronic wound monitoring. Matter 4(8), 2613–2615 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.06.018
- M. Sun, Y. Gu, X. Pei, J. Wang, J. Liu et al., A flexible and wearable epidermal ethanol biofuel cell for on-body and real-time bioenergy harvesting from human sweat. Nano Energy 86, 106061 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106061
- X. He, S. Yang, C. Liu, T. Xu, X. Zhang, Integrated wound recognition in bandages for intelligent treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9(22), e2000941 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000941
- X. Yang, Y. Wang, R. Byrne, G. Schneider, S. Yang, Concepts of artificial intelligence for computer-assisted drug discovery. Chem. Rev. 119(18), 10520–10594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00728
- X. Ni, W. Ouyang, H. Jeong, J.-T. Kim, A. Tzaveils et al., Automated, multiparametric monitoring of respiratory biomarkers and vital signs in clinical and home settings for COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118(19), e2026610118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2026610118
- T. Xu, Y. Song, W. Gao, T. Wu, L.-P. Xu et al., Superwettable electrochemical biosensor toward detection of cancer biomarkers. ACS Sens. 3(1), 72–78 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00868
- L.A. Schneider, A. Korber, S. Grabbe, J. Dissemond, Influence of pH on wound-healing: a new perspective for wound-therapy? Arch. Dermatol. Res. 298(9), 413–420 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-006-0713-x
- M. Wang, Z. Yan, T. Wang, P. Cai, S. Gao et al., Gesture recognition using a bioinspired learning architecture that integrates visual data with somatosensory data from stretchable sensors. Nat. Electron. 3(9), 563–570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-0422-z
- Y. Wang, M. Guo, B. He, B. Gao, Intelligent patches for wound management: in situ sensing and treatment. Anal. Chem. 93(11), 4687–4696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04956
- A. Pal, D. Goswami, H.E. Cuellar, B. Castro, S. Kuang et al., Early detection and monitoring of chronic wounds using low-cost, omniphobic paper-based smart bandages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 117, 696–705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.060
- C. Bansal, R. Scott, D. Stewart, C.J. Cockerell, Decubitus ulcers: a review of the literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 44(10), 805–810 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02636.x
- M.A. Fonder, G.S. Lazarus, D.A. Cowan, B. Aronson-Cook, A.R. Kohli et al., Treating the chronic wound: a practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and wound care dressings. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 58(2), 185–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.048
- J.C. Dumville, N. Stubbs, S.J. Keogh, R.M. Walker, Z. Liu, Hydrogel dressings for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011226.pub2
- E.F. Wywialowski, Tissue perfusion as a key underlying concept of pressure ulcer development and treatment. J. Vasc. Nurs. 17(1), 12–16 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1062-0303(99)90003-1
- J. Besseling, J.J.P. Kastelein, J.C. Defesche, B.A. Hutten, G.K. Hovingh, Association between familial hypercholesterolemia and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 313(10), 1029–1036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.1206
- Y. Liang, M. Li, Y. Yang, L. Qiao, H. Xu et al., pH/glucose dual responsive metformin release hydrogel dressings with adhesion and self-healing via dual-dynamic bonding for athletic diabetic foot wound healing. ACS Nano 16(2), 3194–3207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11040
- S. Wang, H. Zheng, L. Zhou, F. Cheng, Z. Liu et al., Nanoenzyme-reinforced injectable hydrogel for healing diabetic wounds infected with multidrug resistant bacteria. Nano Lett. 20(7), 5149–5158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01371
- Y. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Yang, Y. Fu, L. Huan et al., Thermal responsive sodium alginate/polyacrylamide/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) ionic hydrogel composite via seeding calcium carbonate microps for the engineering of ultrasensitive wearable sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 280, 135909 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135909
- S. Li, L. Wang, W. Zheng, G. Yang, X. Jiang, Rapid fabrication of self-healing, conductive, and injectable gel as dressings for healing wounds in stretchable parts of the body. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(31), 2002370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002370
- D. Simões, S.P. Miguel, M.P. Ribeiro, P. Coutinho, A.G. Mendonça et al., Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: a review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 127, 130–141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.02.022
- J. Qu, X. Zhao, Y. Liang, T. Zhang, P.X. Ma et al., Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 183, 185–199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.044
- M. Shan, X. Chen, X. Zhang, S. Zhang, L. Zhang et al., Injectable conductive hydrogel with self-healing, motion monitoring, and bacteria theranostics for bioelectronic wound dressing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(11), 2303876 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202303876
References
P. Wang, B. Yin, Y.J. Su, C.Y. Jia, Research advances in healing mechanism of chronic refractory wounds mediated by long non-coding RNA. Chin. J. Burn. 36(8), 758–761 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20190526-00254
W. Yue, Y. Guo, J.C. Lee, E. Ganbold, J.K. Wu et al., Advancements in passive wireless sensing systems in monitoring harsh environment and healthcare applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 17(1), 106 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01599-8
M. Rodrigues, N. Kosaric, C.A. Bonham, G.C. Gurtner, Wound healing: a cellular perspective. Physiol. Rev. 99(1), 665–706 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00067.2017
S. Guo, L.A. DiPietro, Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 89(3), 219–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509359125
K. Las Heras, M. Igartua, E. Santos-Vizcaino, R.M. Hernandez, Chronic wounds: current status, available strategies and emerging therapeutic solutions. J. Control. Release 328, 532–550 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.09.039
E.M. Ahmed, Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J. Adv. Res. 6(2), 105–121 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
M. Farahani, A. Shafiee, Wound healing: from passive to smart dressings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10(16), 2100477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202100477
Y. Qiao, J. Luo, T. Cui, H. Liu, H. Tang et al., Soft electronics for health monitoring assisted by machine learning. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01029-1
Q. Pang, D. Lou, S. Li, G. Wang, B. Qiao et al., Smart flexible electronics-integrated wound dressing for real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment of infected wounds. Adv. Sci. 7(6), 1902673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902673
D. Chouhan, N. Dey, N. Bhardwaj, B.B. Mandal, Emerging and innovative approaches for wound healing and skin regeneration: current status and advances. Biomaterials 216, 119267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119267
J. Hu, H. Qian, S. Han, P. Zhang, Y. Lu, Light-activated virtual sensor array with machine learning for non-invasive diagnosis of coronary heart disease. Nano-Micro Lett. 16(1), 274 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-024-01481-7
J. Zhu, H. Zhou, E.M. Gerhard, S. Zhang, F.I. Parra Rodríguez et al., Smart bioadhesives for wound healing and closure. Bioact. Mater. 19, 360–375 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.04.020
M. Falcone, B. De Angelis, F. Pea, A. Scalise, S. Stefani et al., Challenges in the management of chronic wound infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 26, 140–147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2021.05.010
R. Basatneh, B. Najafi, D.G. Armstrong, Health sensors, smart home devices, and the Internet of medical things: an opportunity for dramatic improvement in care for the lower extremity complications of diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 12(3), 577–586 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296818768618
C. Wang, E.S. Sani, W. Gao, Wearable bioelectronics for chronic wound management. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(17), 2111022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202111022
W. Qiu, Q. Wang, M. Li, N. Li, X. Wang et al., 3D hybrid scaffold with aligned nanofiber yarns embedded in injectable hydrogels for monitoring and repairing chronic wounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 234, 109688 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109688
J. Wang, C. Zhao, P. Yang, H. He, Y. Yang et al., A multifunctional electronic dressing with textile-like structure for wound pressure monitoring and treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 679, 737–747 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2024.10.116
X. Liu, S. Tian, S. Xu, W. Lu, C. Zhong et al., A pressure-resistant zwitterionic skin sensor for domestic real-time monitoring and pro-healing of pressure injury. Biosens. Bioelectron. 214, 114528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114528
W. Ma, S. Ling, Y. Liu, Z. Chen, J. Xu, Bio-inspired low-cost fabrication of stretchable, adhesive, transparent, and multi-functionalized joint wound dressings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15(19), 22915–22928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c02065
D. Prakashan, A. Kaushik, S. Gandhi, Smart sensors and wound dressings: artificial intelligence-supported chronic skin monitoring—a review. Chem. Eng. J. 497, 154371 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154371
O. Eskilson, E. Zattarin, L. Berglund, K. Oksman, K. Hanna et al., Nanocellulose composite wound dressings for real-time pH wound monitoring. Mater. Today Bio 19, 100574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100574
Z. Bai, X. Wang, M. Huang, Y. Feng, S. Sun et al., Smart battery-free and wireless bioelectronic platform based on a nature-skin-derived organohydrogel for chronic wound diagnosis, assessment, and accelerated healing. Nano Energy 118, 108989 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108989
P. Mostafalu, A. Tamayol, R. Rahimi, M. Ochoa, A. Khalilpour et al., Smart bandage for monitoring and treatment of chronic wounds. Small 14(33), 1703509 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703509
Y. Zhu, J. Zhang, J. Song, J. Yang, Z. Du et al., A multifunctional pro-healing zwitterionic hydrogel for simultaneous optical monitoring of pH and glucose in diabetic wound treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(6), 1905493 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201905493
Y. Gao, D.T. Nguyen, T. Yeo, S.B. Lim, W.X. Tan et al., A flexible multiplexed immunosensor for point-of-care in situ wound monitoring. Sci. Adv. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abg9614
L. Wang, M. Zhou, T. Xu, X. Zhang, Multifunctional hydrogel as wound dressing for intelligent wound monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134625 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134625
S. Kalasin, P. Sangnuang, W. Surareungchai, Intelligent wearable sensors interconnected with advanced wound dressing bandages for contactless chronic skin monitoring: artificial intelligence for predicting tissue regeneration. Anal. Chem. 94(18), 6842–6852 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00782
J. Jiang, J. Ding, X. Wu, M. Zeng, Y. Tian et al., Flexible and temperature-responsive hydrogel dressing for real-time and remote wound healing monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 11(22), 4934–4945 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB00099K
H. Ma, Z. Liu, X. Lu, S. Zhang, C. Tang et al., 3D printed multi-coupled bioinspired skin-electronic interfaces with enhanced adhesion for monitoring and treatment. Acta Biomater. 187, 183–198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2024.08.048
D. Deng, L. Liang, K. Su, H. Gu, X. Wang et al., Smart hydrogel dressing for machine learning-enabled visual monitoring and promote diabetic wound healing. Nano Today 60, 102559 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102559
M. Wei, H. Wang, C. Chen, G. Fei, D. Yang et al., Conductive, adhesive, and biocompatible hydrogel sensor based on zwitterionic for effective wound healing and monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 506, 160235 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.160235
Z. Li, L.-P. Sun, Y. Tan, Z. Wang, X. Yang et al., Flexible optoelectronic hybrid microfiber long-period grating multimodal sensor. Adv. Sci. 12(17), e2501352 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202501352
B.K. Sun, Z. Siprashvili, P.A. Khavari, Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science 346(6212), 941–945 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1253836
R. Nuccitelli, A role for endogenous electric fields in wound healing. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 58, 1–26 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0070-2153(03)58001-2
C. Korupalli, H. Li, N. Nguyen, F.-L. Mi, Y. Chang et al., Conductive materials for healing wounds: their incorporation in electroactive wound dressings, characterization, and perspectives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10(6), 2001384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202001384
J. Wang, J. Lin, L. Chen, L. Deng, W. Cui, Endogenous electric-field-coupled electrospun short fiber via collecting wound exudation. Adv. Mater. 34(9), e2108325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202108325
X. Zhao, H. Wu, B. Guo, R. Dong, Y. Qiu et al., Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 122, 34–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.011
N.C. Spitzer, Electrical activity in early neuronal development. Nature 444(7120), 707–712 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05300
I. Jun, S. Jeong, H. Shin, The stimulation of myoblast differentiation by electrically conductive sub-micron fibers. Biomaterials 30(11), 2038–2047 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.063
Y. Liang, B. Chen, M. Li, J. He, Z. Yin et al., Injectable antimicrobial conductive hydrogels for wound disinfection and infectious wound healing. Biomacromol 21(5), 1841–1852 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01732
H. Cui, L. Cui, P. Zhang, Y. Huang, Y. Wei et al., In situ electroactive and antioxidant supramolecular hydrogel based on cyclodextrin/copolymer inclusion for tissue engineering repair. Macromol. Biosci. 14(3), 440–450 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201300366
X. Ren, M. Xiao, Y. Xu, Y. Wu, J. Yang et al., Injectable MXene conductive hydrogel improves myocardial infarction through scavenging ROS and repairing myocardium electrical integrity. Chem. Eng. J. 481, 148791 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.148791
W. Liu, N. Zhao, Q. Yin, X. Zhao, K. Guo et al., Injectable hydrogels encapsulating dual-functional Au@Pt core-shell nanops regulate infarcted microenvironments and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of stem cells through antioxidant and electrical integration. ACS Nano 17(3), 2053–2066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c07436
L. Nie, Q. Wei, J. Li, Y. Deng, X. He et al., Fabrication and desired properties of conductive hydrogel dressings for wound healing. RSC Adv. 13(13), 8502–8522 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA07195A
L. Lipani, B.G.R. Dupont, F. Doungmene, F. Marken, R.M. Tyrrell et al., Non-invasive, transdermal, path-selective and specific glucose monitoring via a graphene-based platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13(6), 504–511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0112-4
A. McLister, J. McHugh, J. Cundell, J. Davis, New developments in smart bandage technologies for wound diagnostics. Adv. Mater. 28(27), 5732–5737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201504829
X. Wang, H. Huo, C. Xu, H. Lin, Q. Wang et al., A sensitive non-enzymatic dual-conductive biosensor for continuous glucose monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 1279, 341845 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341845
K. Shen, Z. Liu, R. Xie, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang et al., Nanocomposite conductive hydrogels with Robust elasticity and multifunctional responsiveness for flexible sensing and wound monitoring. Mater. Horiz. 10(6), 2096–2108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MH00192J
Z. Qin, X. Sun, Q. Yu, H. Zhang, X. Wu et al., Carbon nanotubes/hydrophobically associated hydrogels as ultrastretchable, highly sensitive, stable strain, and pressure sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(4), 4944–4953 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21659
M.F.L. De Volder, S.H. Tawfick, R.H. Baughman, A.J. Hart, Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339(6119), 535–539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222453
H. Cai, D. Zhang, H. Zhang, M. Tang, Z. Xu et al., Trehalose-enhanced ionic conductive hydrogels with extreme stretchability, self-adhesive and anti-freezing abilities for both flexible strain sensor and all-solid-state supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 472, 144849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.144849
Z. Xu, X. Qiao, R. Tao, Y. Li, S. Zhao et al., A wearable sensor based on multifunctional conductive hydrogel for simultaneous accurate pH and tyrosine monitoring in sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 234, 115360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115360
X. Fan, L. Zhao, Q. Ling, J. Liu, H. Gu, Mussel-induced nano-silver antibacterial, self-healing, self-adhesive, anti-freezing, and moisturizing dual-network organohydrogel based on SA-PBA/PVA/CNTs as flexible wearable strain sensors. Polymer 256, 125270 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125270
J. Wang, W. Liu, G. Luo, Z. Li, C. Zhao et al., Synergistic effect of well-defined dual sites boosting the oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 11(12), 3375–3379 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EE02656D
H. Sun, Y. Zhao, S. Jiao, C. Wang, Y. Jia et al., Environment tolerant conductive nanocomposite organohydrogels as flexible strain sensors and power sources for sustainable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(24), 2101696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202101696
W.-L. Lei, C.-W. Peng, S.-C. Chiu, H.-E. Lu, C.-W. Wu et al., All biodisintegratable hydrogel biohybrid neural interfaces with synergistic performances of microelectrode array technologies, tissue scaffolding, and cell therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(3), 2307365 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202307365
F. He, X. You, H. Gong, Y. Yang, T. Bai et al., Stretchable, biocompatible, and multifunctional silk fibroin-based hydrogels toward wearable strain/pressure sensors and triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(5), 6442–6450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b19721
Z. Tu, M. Chen, M. Wang, Z. Shao, X. Jiang et al., Engineering bioactive M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial scaffolds for rapid angiogenesis and diabetic wound repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(30), 2100924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202100924
L. Geng, W. Liu, B. Fan, J. Wu, S. Shi et al., Anisotropic double-network hydrogels integrated superior performance of strength, toughness and conductivity for flexible multi-functional sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 462, 142226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142226
Y. Zhang, J. Zou, S. Wang, X. Hu, Z. Liu et al., Tailoring nanostructured MXene to adjust its dispersibility in conductive hydrogel for self-powered sensors. Compos. Part B Eng. 272, 111191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2024.111191
Y. Zhang, Z. Xu, Y. Yuan, C. Liu, M. Zhang et al., Flexible antiswelling photothermal-therapy MXene hydrogel-based epidermal sensor for intelligent human–machine interfacing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(21), 2300299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202300299
J. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Zhou, S. Zhu, C. Gao et al., A multifunctional sensor for real-time monitoring and pro-healing of frostbite wounds. Acta Biomater. 172, 330–342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2023.10.003
B. Song, X. Fan, J. Shen, H. Gu, Ultra-stable and self-healing coordinated collagen-based multifunctional double-network organohydrogel e-skin for multimodal sensing monitoring of strain-resistance, bioelectrode, and self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator. Chem. Eng. J. 474, 145780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145780
Y. Zhao, Z. Li, S. Song, K. Yang, H. Liu et al., Skin-inspired antibacterial conductive hydrogels for epidermal sensors and diabetic foot wound dressings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(31), 1901474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901474
X. Wang, H. Huo, Y. Zhong, Y. Yang, H. Lin et al., Synergistic antimicrobial glycyrrhizic acid-based functional biosensing composite for sensitive glucose monitoring and collaborative wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(20), 2400580 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202400580
Y. Zhang, S. Li, Z. Gao, D. Bi, N. Qu et al., Highly conductive and tough polyacrylamide/sodium alginate hydrogel with uniformly distributed polypyrrole nanospheres for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 315, 120953 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120953
J. Xu, H. Zhang, Z. Guo, C. Zhang, H. Tan et al., Fully physical crosslinked BSA-based conductive hydrogels with high strength and fast self-recovery for human motion and wireless electrocardiogram sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 230, 123195 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123195
H. Zheng, M. Chen, Y. Sun, B. Zuo, Self-Healing, Wet-Adhesion silk fibroin conductive hydrogel as a wearable strain sensor for underwater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136931 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136931
H. He, H. Li, A. Pu, W. Li, K. Ban et al., Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 14(1), 759 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36438-8
H. Liu, Z. Li, S. Che, Y. Feng, L. Guan et al., A smart hydrogel patch with high transparency, adhesiveness and hemostasis for all-round treatment and glucose monitoring of diabetic foot ulcers. J. Mater. Chem. B 10(30), 5804–5817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TB01048H
L.S. Devi, R.P. Palathinkal, A.K. Dasmahapatra, Preparation of cross-linked PANI/PVA conductive hydrogels for electrochemical energy storage and sensing applications. Polymer 293, 126673 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2024.126673
H. Zhang, H. Shen, J. Lan, H. Wu, L. Wang et al., Dual-network polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan-grafted-polyaniline conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 295, 119848 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119848
L. Xiao, F. Hui, T. Tian, R. Yan, J. Xin et al., A novel conductive antibacterial nanocomposite hydrogel dressing for healing of severely infected wounds. Front. Chem. 9, 787886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.787886
X. Peng, W. Wang, W. Yang, J. Chen, Q. Peng et al., Stretchable, compressible, and conductive hydrogel for sensitive wearable soft sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 618, 111–120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.03.037
G. Li, K. Huang, J. Deng, M. Guo, M. Cai et al., Highly conducting and stretchable double-network hydrogel for soft bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 34(15), 2200261 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202200261
C. Zhang, M. Wang, C. Jiang, P. Zhu, B. Sun et al., Highly adhesive and self-healing γ-PGA/PEDOT: PSS conductive hydrogels enabled by multiple hydrogen bonding for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 95, 106991 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.106991
Y. Shin, H.S. Lee, J.-U. Kim, Y.-H. An, Y.-S. Kim et al., Functional-hydrogel-based electronic-skin patch for accelerated healing and monitoring of skin wounds. Biomaterials 314, 122802 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122802
Y. Wang, L. Sun, G. Chen, H. Chen, Y. Zhao, Structural color ionic hydrogel patches for wound management. ACS Nano 17(2), 1437–1447 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c10142
W. Zou, Y. Zhou, S. Zhong, F. Liao, J. Lu et al., Biomimetic FeNi-MOF assisted intelligent theranostic hydrogels for pH identification and treatment of wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 497, 154945 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154945
H. Zhang, H. Hu, Y. Dai, L. Xin, Q. Pang et al., A conductive multifunctional hydrogel dressing with the synergistic effect of ROS-scavenging and electroactivity for the treatment and sensing of chronic diabetic wounds. Acta Biomater. 167, 348–360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.045
H.-M. Zhang, Y.-P. Wang, S.-F. Zhang, W.-B. Niu, Heterogeneous structural color conductive photonic organohydrogel fibers with alternating single and dual networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(49), 54936–54945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c16191
X. Zhang, H. Geng, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Hao et al., Modulation of double-network hydrogels via seeding calcium carbonate microps for the engineering of ultrasensitive wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 11(6), 2996–3007 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TA07834A
Y.-H. Lin, Y.-C. Chen, K.-S. Cheng, P.-J. Yu, J.-L. Wang et al., Higher periwound temperature associated with wound healing of pressure ulcers detected by infrared thermography. J. Clin. Med. 10(13), 2883 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132883
N. Kučišec-Tepeš, Characteristic features of pressure ulcer infection. Acta Med. Croat. 70(Suppl 1), 45–51 (2016). (PMID: 29087671)
N. Li, Y. Li, Z. Cheng, Y. Liu, Y. Dai et al., Bioadhesive polymer semiconductors and transistors for intimate biointerfaces. Science 381(6658), 686–693 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg8758
J.L. Ramirez-GarciaLuna, R. Bartlett, J.E. Arriaga-Caballero, R.D.J. Fraser, G. Saiko, Infrared thermography in wound care, surgery, and sports medicine: a review. Front. Physiol. 13, 838528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.838528
F.R. Ávila, M.T. Huayllani, D. Boczar, P. Ciudad, R. Sarabia-Estrada et al., Materiales sensibles a biomarcadores y apósitos inteligentes: revisión sistemática. J. Wound Care 29(LatAm sup 3), 13–22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2020.29.LatAm_sup_3.13
T. Kanazawa, A. Kitamura, G. Nakagami, T. Goto, T. Miyagaki et al., Lower temperature at the wound edge detected by thermography predicts undermining development in pressure ulcers: a pilot study. Int. Wound J. 13(4), 454–460 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12454
F.-Q. Yang, L. Ge, Colorimetric sensors: methods and applications. Sensors 23(24), 9887 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249887
F. Mo, P. Zhou, S. Lin, J. Zhong, Y. Wang, A review of conductive hydrogel-based wearable temperature sensors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(26), e2401503 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202401503
H. Chen, J. Huang, J. Liu, J. Gu, J. Zhu et al., High toughness multifunctional organic hydrogels for flexible strain and temperature sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 9(40), 23243–23255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA07127K
X. Dang, Y. Fu, X. Wang, Versatile biomass-based injectable photothermal hydrogel for integrated regenerative wound healing and skin bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34(42), 2405745 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202405745
M.-H. Schmid-Wendtner, H.C. Korting, The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier function. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 19(6), 296–302 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1159/000094670
S.L. Percival, S. McCarty, J.A. Hunt, E.J. Woods, The effects of pH on wound healing, biofilms, and antimicrobial efficacy. Wound Repair Regen. 22(2), 174–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.12125
Q. Dou, Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Wang, D. Hu et al., Ultrasensitive poly(boric acid) hydrogel-coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor by using UV pressing-assisted polymerization for saliva glucose monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(30), 34190–34197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c08229
H. Guo, M. Bai, C. Wen, M. Liu, S. Tian et al., A Zwitterionic-Aromatic Motif-Based ionic skin for highly biocompatible and Glucose-Responsive sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 561–571 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.012
P. Martin, Wound healing: aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276(5309), 75–81 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5309.75
B. Hajhosseini, M.T. Longaker, G.C. Gurtner, Pressure injury. Ann. Surg. 271(4), 671–679 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000003567
G.S. Schultz, R.G. Sibbald, V. Falanga, E.A. Ayello, C. Dowsett et al., Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair Regen. 11(s1), S1–S28 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-475X.11.s2.1.x
Q. Zeng, X. Qi, G. Shi, M. Zhang, H. Haick, Wound dressing: from nanomaterials to diagnostic dressings and healing evaluations. ACS Nano 16(2), 1708–1733 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c08411
Q. Wang, W. Qiu, H. Liu, X. Li, X. Qin et al., Conductive hydrogel dressings based on cascade reactions with photothermal effect for monitoring and treatment of diabetic wounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 242, 110098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110098
S.-J. Ge, X.-J. Zhou, S.-L. Liu, M. Xu, Y. Shi et al., Multifunctional all hydrogel-based smart dressing system fabricated by a self-healing cross-linking strategy for real-time monitoring of wound temperature, strain and on-demand drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. C 10(45), 17084–17098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TC03887K
A. Kekonen, M. Bergelin, J.-E. Eriksson, A. Vaalasti, H. Ylänen et al., Bioimpedance method for monitoring venous ulcers: Clinical proof-of-concept study. Biosens. Bioelectron. 178, 112974 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.112974
S.L. Swisher, M.C. Lin, A. Liao, E.J. Leeflang, Y. Khan et al., Impedance sensing device enables early detection of pressure ulcers in vivo. Nat. Commun. 6, 6575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7575
J. Cao, P. Wu, Q. Cheng, C. He, Y. Chen et al., Ultrafast fabrication of self-healing and injectable carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel dressing for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(20), 24095–24105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c02089
L. Zhao, L. Niu, H. Liang, H. Tan, C. Liu et al., pH and glucose dual-responsive injectable hydrogels with insulin and fibroblasts as bioactive dressings for diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(43), 37563–37574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09395
O. Simoska, J. Duay, K.J. Stevenson, Electrochemical detection of multianalyte biomarkers in wound healing efficacy. ACS Sens. 5(11), 3547–3557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01697
J. Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. Lee, J. Hua, S. Li et al., A pulsatile release platform based on photo-induced imine-crosslinking hydrogel promotes scarless wound healing. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1670 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21964-0
S. Du, N. Zhou, Y. Gao, G. Xie, H. Du et al., Bioinspired hybrid patches with self-adhesive hydrogel and piezoelectric nanogenerator for promoting skin wound healing. Nano Res. 13(9), 2525–2533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2891-9
L. Mao, S. Hu, Y. Gao, L. Wang, W. Zhao et al., Biodegradable and electroactive regenerated bacterial cellulose/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) composite hydrogel as wound dressing for accelerating skin wound healing under electrical stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9(19), 2000872 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000872
B. Qiao, Q. Pang, P. Yuan, Y. Luo, L. Ma, Smart wound dressing for infection monitoring and NIR-triggered antibacterial treatment. Biomater. Sci. 8(6), 1649–1657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm02060h
E.S. Sani, C. Wang, W. Gao, A soft bioaffinity sensor array for chronic wound monitoring. Matter 4(8), 2613–2615 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.06.018
M. Sun, Y. Gu, X. Pei, J. Wang, J. Liu et al., A flexible and wearable epidermal ethanol biofuel cell for on-body and real-time bioenergy harvesting from human sweat. Nano Energy 86, 106061 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106061
X. He, S. Yang, C. Liu, T. Xu, X. Zhang, Integrated wound recognition in bandages for intelligent treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9(22), e2000941 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000941
X. Yang, Y. Wang, R. Byrne, G. Schneider, S. Yang, Concepts of artificial intelligence for computer-assisted drug discovery. Chem. Rev. 119(18), 10520–10594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00728
X. Ni, W. Ouyang, H. Jeong, J.-T. Kim, A. Tzaveils et al., Automated, multiparametric monitoring of respiratory biomarkers and vital signs in clinical and home settings for COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118(19), e2026610118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2026610118
T. Xu, Y. Song, W. Gao, T. Wu, L.-P. Xu et al., Superwettable electrochemical biosensor toward detection of cancer biomarkers. ACS Sens. 3(1), 72–78 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00868
L.A. Schneider, A. Korber, S. Grabbe, J. Dissemond, Influence of pH on wound-healing: a new perspective for wound-therapy? Arch. Dermatol. Res. 298(9), 413–420 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-006-0713-x
M. Wang, Z. Yan, T. Wang, P. Cai, S. Gao et al., Gesture recognition using a bioinspired learning architecture that integrates visual data with somatosensory data from stretchable sensors. Nat. Electron. 3(9), 563–570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-0422-z
Y. Wang, M. Guo, B. He, B. Gao, Intelligent patches for wound management: in situ sensing and treatment. Anal. Chem. 93(11), 4687–4696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04956
A. Pal, D. Goswami, H.E. Cuellar, B. Castro, S. Kuang et al., Early detection and monitoring of chronic wounds using low-cost, omniphobic paper-based smart bandages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 117, 696–705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.060
C. Bansal, R. Scott, D. Stewart, C.J. Cockerell, Decubitus ulcers: a review of the literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 44(10), 805–810 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02636.x
M.A. Fonder, G.S. Lazarus, D.A. Cowan, B. Aronson-Cook, A.R. Kohli et al., Treating the chronic wound: a practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and wound care dressings. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 58(2), 185–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.048
J.C. Dumville, N. Stubbs, S.J. Keogh, R.M. Walker, Z. Liu, Hydrogel dressings for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011226.pub2
E.F. Wywialowski, Tissue perfusion as a key underlying concept of pressure ulcer development and treatment. J. Vasc. Nurs. 17(1), 12–16 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1062-0303(99)90003-1
J. Besseling, J.J.P. Kastelein, J.C. Defesche, B.A. Hutten, G.K. Hovingh, Association between familial hypercholesterolemia and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 313(10), 1029–1036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.1206
Y. Liang, M. Li, Y. Yang, L. Qiao, H. Xu et al., pH/glucose dual responsive metformin release hydrogel dressings with adhesion and self-healing via dual-dynamic bonding for athletic diabetic foot wound healing. ACS Nano 16(2), 3194–3207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11040
S. Wang, H. Zheng, L. Zhou, F. Cheng, Z. Liu et al., Nanoenzyme-reinforced injectable hydrogel for healing diabetic wounds infected with multidrug resistant bacteria. Nano Lett. 20(7), 5149–5158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01371
Y. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Yang, Y. Fu, L. Huan et al., Thermal responsive sodium alginate/polyacrylamide/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) ionic hydrogel composite via seeding calcium carbonate microps for the engineering of ultrasensitive wearable sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 280, 135909 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135909
S. Li, L. Wang, W. Zheng, G. Yang, X. Jiang, Rapid fabrication of self-healing, conductive, and injectable gel as dressings for healing wounds in stretchable parts of the body. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(31), 2002370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002370
D. Simões, S.P. Miguel, M.P. Ribeiro, P. Coutinho, A.G. Mendonça et al., Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: a review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 127, 130–141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.02.022
J. Qu, X. Zhao, Y. Liang, T. Zhang, P.X. Ma et al., Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 183, 185–199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.044
M. Shan, X. Chen, X. Zhang, S. Zhang, L. Zhang et al., Injectable conductive hydrogel with self-healing, motion monitoring, and bacteria theranostics for bioelectronic wound dressing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13(11), 2303876 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202303876